Brand Control, Part 2: “Born to Stand Out” — Choosing a Trade Mark That Can Actually Be Registered
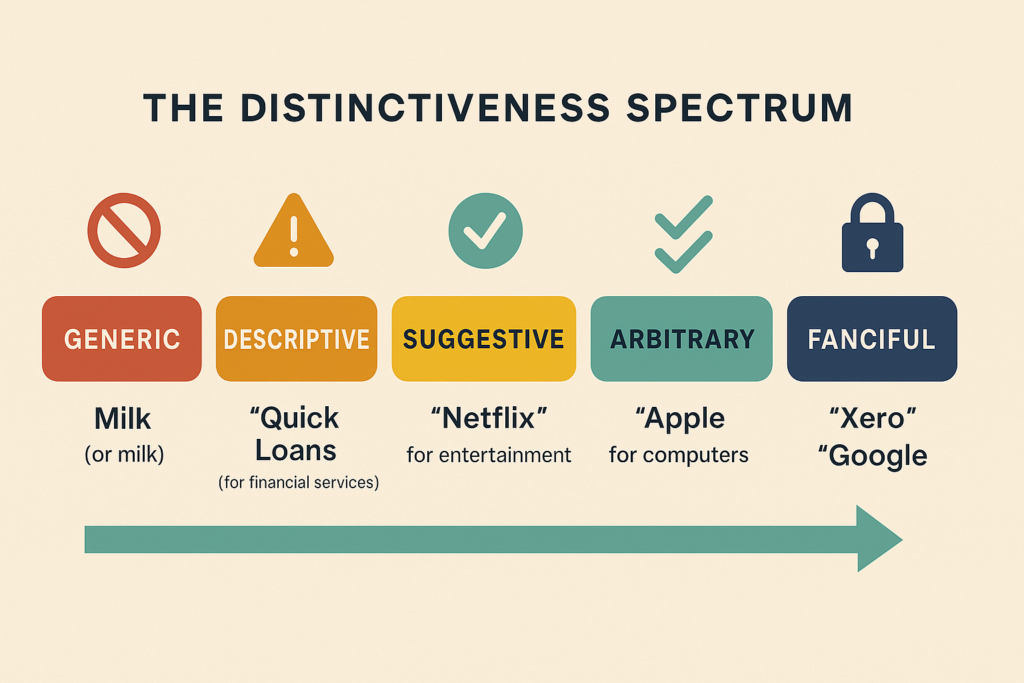 Not every brand name is created equal. In the eyes of the law, the more descriptive your mark, the weaker your rights.
Not every brand name is created equal. In the eyes of the law, the more descriptive your mark, the weaker your rights.
That might sound counterintuitive — especially to marketers and founders who want a brand name that says exactly what the business does. But from a trade mark perspective, the best brand names do more than describe — they distinguish.
The Distinctiveness Spectrum
Trade mark registrability hinges on one core concept: distinctiveness. The more distinctive a mark is, the more likely it is to be accepted by IP Australia — and the easier it will be to enforce down the track.
You can think of trade marks as falling on a distinctiveness spectrum:
-
Generic terms (like Milk for milk) are never registrable. They’re the language of the trade, not a badge of origin.
-
Descriptive marks (like Quick Loans for a lending service) are difficult to register unless you can prove long and widespread use that’s made the name distinctive over time.
-
Suggestive marks (like Netflix for entertainment) can sometimes succeed if they require a leap of imagination and aren’t used commonly in the industry.
-
Arbitrary marks (like Apple for computers) are legally strong — because they don’t describe the goods at all.
-
Fanciful marks (like Xero or Google) are invented words. These tend to be the strongest of all: highly protectable and uniquely tied to their brand.
Common Pitfalls When Picking a Name
Some names feel brand-like but run into trouble at the registration stage. Here are a few traps to watch for:
-
Geographic references: A name like Brisbane Plumbing Services might be accurate, but it’s also highly descriptive and hard to protect. It tells people what you do and where — but not who you are.
-
Industry terms: A name like LegalEdge might sound sharp, but if it clearly relates to legal services, it may lack the distinctiveness needed for registration — especially if similar names are already on the register.
-
Foreign language words: Just because a word isn’t in English doesn’t mean it’s distinctive. If the translation is something generic (like Dolce, which means “sweet”), it may still be treated as descriptive.
-
Initialisms and acronyms: These can be difficult to protect unless the public has come to associate them with your business (think IBM or ANZ). Until then, they often get treated as meaningless strings of letters.
💡 IP Mojo Tip
If your brand name tells your whole story at first glance, there’s a good chance it’s too descriptive to protect. Aim for memorability, not just meaning. A good trade mark doesn’t explain — it sticks.
 The long-running IP clash between Australian designer Katie Taylor (aka Katie Perry) and US popstar Katheryn Hudson (aka Katy Perry) has now reached the High Court. Both sides have filed their submissions—and the gloves are well and truly off.
The long-running IP clash between Australian designer Katie Taylor (aka Katie Perry) and US popstar Katheryn Hudson (aka Katy Perry) has now reached the High Court. Both sides have filed their submissions—and the gloves are well and truly off. When most people talk about a “brand”, they’re really thinking about a vibe: a gut-level feel, a cultural footprint, an aesthetic. And all of that matters — but from a legal perspective, a brand only really lives and breathes through what you can protect.
When most people talk about a “brand”, they’re really thinking about a vibe: a gut-level feel, a cultural footprint, an aesthetic. And all of that matters — but from a legal perspective, a brand only really lives and breathes through what you can protect. In the world of IP, form usually follows function—until it tries to live forever.
In the world of IP, form usually follows function—until it tries to live forever. The Case in Brief
The Case in Brief Launching a brand? Running a business? Advising one? Then you already know the power of a strong name, logo, or tagline. But what makes a brand not just memorable — but legally defensible?
Launching a brand? Running a business? Advising one? Then you already know the power of a strong name, logo, or tagline. But what makes a brand not just memorable — but legally defensible? Firstmac’s long-running dispute with Zip Co over the word “ZIP” has taken another sharp turn—this time with Zip Co applying for special leave to appeal to the High Court.
Firstmac’s long-running dispute with Zip Co over the word “ZIP” has taken another sharp turn—this time with Zip Co applying for special leave to appeal to the High Court.